CZhang IT12
Friday, June 14, 2019
Thursday, June 13, 2019
Game Journalism Play 3
Game Journalism Play 3
1. What NEW things did you build today? [IMAGE]
I build a bird nest today, it gives me feathers.
2. How will these NEW things help you play the game (TIPS&TRICKS)?
It attracts birds and left me with feathers and eggs. The feathers can be used to build things such as an upgraded bed. The eggs are really nutritious, it boost up the hunger bar and the water bar for me.
3. What strategies are you going to try to focus on tomorrow?
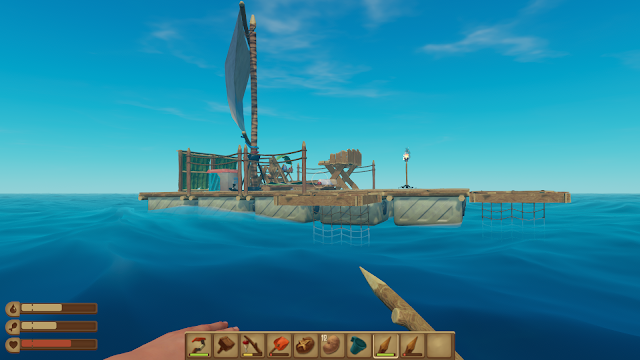
I will be focusing on building a melter to get vine gods from seaweeds and metal bricks from metal ore. But I also have to gather lots of woods, so that I can afford to run the melter.4. Add a picture of your raft. (include a caption)
Explain why you built the raft the way you did.
I build the raft this way because I will not lose anything even if a shark attacks me. Since the out range of the raft is wrapped with foundations.
1. What NEW things did you build today? [IMAGE]
I build a bird nest today, it gives me feathers.
2. How will these NEW things help you play the game (TIPS&TRICKS)?
It attracts birds and left me with feathers and eggs. The feathers can be used to build things such as an upgraded bed. The eggs are really nutritious, it boost up the hunger bar and the water bar for me.
3. What strategies are you going to try to focus on tomorrow?
I will be focusing on building a melter to get vine gods from seaweeds and metal bricks from metal ore. But I also have to gather lots of woods, so that I can afford to run the melter.4. Add a picture of your raft. (include a caption)
Explain why you built the raft the way you did.
I build the raft this way because I will not lose anything even if a shark attacks me. Since the out range of the raft is wrapped with foundations.
Game Journalism Work Day 3 - Build More
Game Journalism Work Day 3 - Build More
Use (IMAGEs) to display each of the 7 options.
A support pole
A wall that is similar to a fence, prevent you from falling, can build decorations o there as well
A fence that doesn't block your view and still work as a fence
Stairs
helps you to get onto an island or having a second floor on your raft.
helps you to get onto an island or having a second floor on your raft.
Roof
Gives you shade and blocks the rain
Repair
After being attacked by a shark, use this to repair it
- a research table - (IMAGE)
- a Net - (IMAGE)
Helps you collect the resources
- scare crow - (IMAGE)
- A second level - (IMAGE)
- shark bait -Shark eating Shark bait [VIDEO]
- foraging on an Island - (IMAGE)
Game Journalism Play Day 2
Game Journalism Play Day 2
1. What specifically did you do today?I build more onto the raft, I started to move things to the second floor so that it is more safe, I also build more storage as I gathered more and more resources. Then I fished more often so that I always have food left. I also put spare or I should say back up resources in the storages, just in case I died on a trip to under water.
2. What did you learn about how to play the game (TIPS&TRICKS)?
I learn to plan out everything well in this game. Because if nothing is planned you will kind of be confused about what is going on, and how to make the raft better. So my trick when I kinda get confused is to put things in the storage, then deal with it when I get my mind back.3. What strategies are you going to try to focus on tomorrow?
I will be focusing on finding islands, so that I can collect more sand and clays to make bricks to build a melter.4. Add a picture of your raft. (include a caption) Explain what you have done to your raft and WHY.
This is my raft right now, it looks plain but stable. As you can see, the surrounding of the raft is empty, because that will save my life when I am being attacked by a shark. I will be able to get on any side of the raft.
Friday, June 7, 2019
Game Journalism Play Day 1
Game Journalism Play Day 1
1. What specifically did you do?
I used this whole day to collect resources and build tools and things that I need to survive, which is building a water purifier and a basic grill. I also build a storage because I noticed that I cannot carry all the resources with me throughout the game. The I build the fishing rod and the wooden stick, so that I can get myself food and also use the wooden stick to protect myself if a shark attacks me.
2. What did you learn about how to play the game? (Tips and Tricks)
2. What did you learn about how to play the game? (Tips and Tricks)
I learned to prioritize things in the game, because with limited resources, it is not possible to get all the tools made. So it is important to know how to choose which tool to make first. And also to store things in the storage because in case anything happens, you'll still have resources to start over again.3. What strategies are you going to try to focus on tomorrow? I will be focusing on building onto the raft, as the more space you have, the more things you can do on it.4. Add a picture of your raft that includes a description
I started building a second floor so that it can help me get onto an island if I get close to one. But so far, it has all the basic things like the water purifier, the grill, storage and a bed.
Game Journalism Work Day 1 - Basics
Game Journalism Work Day 1 - Basics
Introduction of the game:
This game is basically about surviving in the middle of the ocean starting with a small raft. And then slowly build up to a fancy raft and explore more resources. The weird thing is that the resources are just in the middle of the ocean floating. I wonder where it came from.
How to collect debris?
We use the hook. You basically just hold it, aim and let go to get the stuffs. Also if the resources floats close to or under the raft, you are able to just press E to collect it.
- Your raft [IMAGE]
- each type of debris [IMAGE] -what's it good for?
The main debris that we need is wood, leaf, plastic and scrap. Wood can be use to build onto the craft. Leaf can be make into rope, which can be used to build tools. Plastic can also be use to build foundations and tools. Scrap is the most rare one among the four, it does not float on the ocean by itself. It only comes in the barriers, it can be make into nails, which is another more advantaged resources.
- a shark eating your raft [IMAGE]
I DID NOT DIE!! YAAAY!!!
Friday, May 31, 2019
SQL Summary(3)
SQL Summary(3)
Stored Procedure
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP)
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) manages transaction based applications which can be used for data entry, data retrieval and data processing. OLTP makes data management simple and efficient. Unlike OLAP systems goal of OLTP systems is serving real-time transactions. An example will be shopping online and use card to pay for it on a transaction webpage.
CLAUSE
SQL clause is defined to limit the result set by providing condition to the query. This usually filters some rows from the whole set of records.
I think this three is the most important one and the ones that are the most connected to our daily life. As this three affects online shopping, the storage of the device and also cloud disks.
What I'll be doing tomorrow?
I will be reviewing more SQL summaries tomorrow.
May--->June Post
May--->June Post
In May, I have tried to master another programming language which is SQL. SQL is a language that allows programmers to set up tables in rows. This language is useful for statistic, as it allows you to find what you want easily in simple codes. However, after I did the quiz, I noticed that I am not fully mastered in the theories about the language. But I think I am still able to use the codes correctly if I need to.
In June, Since this is going to be a short month. I am planning to post things about the website that I was trying to working on on Sublime Text on my laptop. I am stuck with the structure and classes of the website at the moment, but I believe that I will be able to overcome this soon. And I will be posting pictures about the process。
SQL Summary(4)
SQL Summary(4)
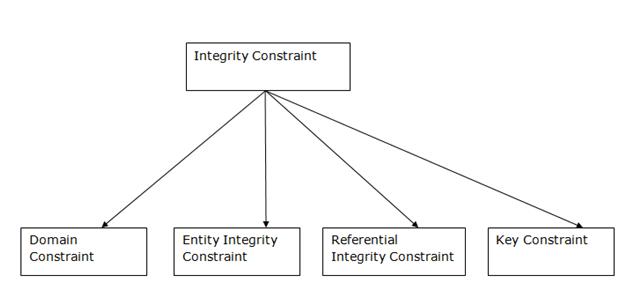
Data Integrity
Data Integrity defines the accuracy and consistency of data stored in a database. It can also define integrity constraints to enforce business rules on the data when it is entered into the application or database.

Auto Increment
Auto increment keyword allows the user to create a unique number to be generated when a new record is inserted into the table. AUTO INCREMENT keyword can be used in Oracle and IDENTITY keyword can be used in SQL SERVER. Mostly this keyword can be used whenever PRIMARY KEY is used.
Cluster and Non-Cluster Index
Clustered index is used for easy retrieval of data from the database by altering the way that the records are stored. Database sorts out rows by the column which is set to be clustered index.
A nonclustered index does not alter the way it was stored but creates a complete separate object within the table. It point back to the original table rows after searching.
Datawarehouse
Datawarehouse is a central repository of data from multiple sources of information. Those data are consolidated, transformed and made available for the mining and online processing. Warehouse data have a subset of data called Data Marts.

Joins
- Self-join is set to be query used to compare to itself. This is used to compare values in a column with other values in the same column in the same table. ALIAS ES can be used for the same table comparison.
- Cross join defines as Cartesian product where number of rows in the first table multiplied by number of rows in the second table. If suppose, WHERE clause is used in cross join then the query will work like an INNER JOIN.
User defined functions
User defined functions are the functions written to use that logic whenever required. It is not necessary to write the same logic several times. Instead, function can be called or executed whenever needed.
- Scalar Functions.
- Inline Table valued functions.
- Multi statement valued functions.
Collation
Collation is defined as set of rules that determine how character data can be sorted and compared. This can be used to compare A and, other language characters and also depends on the width of the characters. ASCII value can be used to compare these character data.
Types of collation sensitivity
- Case Sensitivity – A and a and B and b.
- Accent Sensitivity.
- Kana Sensitivity – Japanese Kana characters.
- Width Sensitivity – Single byte character and double byte character.
Why did I take all these notes?
The reason why I took these notes is because of a SQL quiz that I took. I got a lot of it wrong after just taking lessons from Codecademy. And so, I looked up the lesson page for the quiz that I took which is from a few different websites. Which includes w3schools and other ones. The key words and points in these three summaries that I wrote are all the important notes that should be memorized for doing other SQL quizzes.
Wednesday, May 29, 2019
SQL Summary(2)
SQL Summary(2)
View
A view is a virtual table which consists of a subset of data contained in a table. Views are not virtually present, and it takes less space to store. View can have data of one or more tables combined, and it is depending on the relationship.
Index
An index is performance tuning method of allowing faster retrieval of records from the table. An index creates an entry for each value and it will be faster to retrieve data.
Indexes
Unique Index
This indexing does not allow the field to have duplicate values if the column is unique indexed. Unique index can be applied automatically when primary key is defined.
A view is a virtual table which consists of a subset of data contained in a table. Views are not virtually present, and it takes less space to store. View can have data of one or more tables combined, and it is depending on the relationship.
Index
An index is performance tuning method of allowing faster retrieval of records from the table. An index creates an entry for each value and it will be faster to retrieve data.
Indexes
- Clustered Index
This type of index reorders the physical order of the table and search based on the key values. Each table can have only one clustered index.
- NonClustered Index
NonClustered Index does not alter the physical order of the table and maintains logical order of data. Each table can have 999 nonclustered indexes.
Cursor
A database Cursor is a control which enables traversal over the rows or records in the table. This can be viewed as a pointer to one row in a set of rows. Cursor is very much useful for traversing such as retrieval, addition and removal of database records.
Database Relationships
- One to One Relationship.
- One to Many Relationship.
- Many to One Relationship.
- Self-Referencing Relationship.
DB query
A DB query is a code written in order to get the information back from the database. Query can be designed in such a way that it matched with our expectation of the result set. Simply, a question to the Database.
Subquery
A subquery is a query within another query. The outer query is called as main query, and inner query is called subquery. SubQuery is always executed first, and the result of subquery is passed on to the main query.
- A correlated subquery cannot be considered as independent query, but it can refer the column in a table listed in the FROM the list of the main query.
- A Non-Correlated subquery can be considered as independent query and the output of subquery are substituted in the main query.
Stored procedure
Stored Procedure is a function consists of many SQL statement to access the database system. Several SQL statements are consolidated into a stored procedure and execute them whenever and wherever required.
DB trigger
A DB trigger is a code or programs that automatically execute with response to some event on a table or view in a database. Mainly, trigger helps to maintain the integrity of the database.


What is the difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE commands?
DELETE command is used to remove rows from the table, and WHERE clause can be used for conditional set of parameters. Commit and Rollback can be performed after delete statement.
TRUNCATE removes all rows from the table. Truncate operation cannot be rolled back.
What are local and global variables and their differences?
Local variables are the variables which can be used or exist inside the function. They are not known to the other functions and those variables cannot be referred or used. Variables can be created whenever that function is called.
Global variables are the variables which can be used or exist throughout the program. Same variable declared in global cannot be used in functions. Global variables cannot be created whenever that function is called.
Constraint
Constraint can be used to specify the limit on the data type of table. Constraint can be specified while creating or altering the table statement. Sample of constraint are.
- NOT NULL.
- CHECK.
- DEFAULT.
- UNIQUE.
- PRIMARY KEY.
- FOREIGN KEY.
What I'll be doing tomorrow?
I will be continuing doing the SQL summary and reasons will be explained why I am doing this summary.
I will be continuing doing the SQL summary and reasons will be explained why I am doing this summary.
Tuesday, May 28, 2019
SQL Summary(1)
SQL Summary(1)
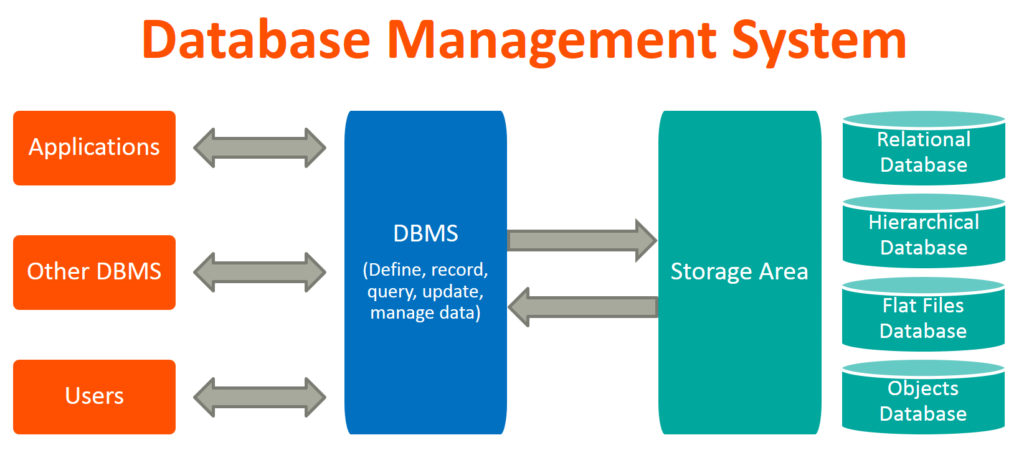
DBMS
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a program that controls creation, maintenance and use of a database. DBMS can be termed as File Manager that manages data in a database rather than saving it in file systems.
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a program that controls creation, maintenance and use of a database. DBMS can be termed as File Manager that manages data in a database rather than saving it in file systems.
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. RDBMS store the data into the collection of tables, which is related by common fields between the columns of the table. It also provides relational operators to manipulate the data stored into the tables.
Database
Database is nothing but an organized form of data for easy access, storing, retrieval and managing of data. This is also known as structured form of data which can be accessed in many ways.
KEYS
- Primary key
A primary key is a combination of fields which uniquely specify a row. This is a special kind of unique key, and it has implicit NOT NULL constraint. It means, Primary key values cannot be NULL.
- Unique key
A Unique key constraint uniquely identified each record in the database. This provides uniqueness for the column or set of columns.
- Foreign key
A foreign key is one table which can be related to the primary key of another table. Relationship needs to be created between two tables by referencing foreign key with the primary key of another table.
JOINS
- Inner Join
Inner join return rows when there is at least one match of rows between the tables.
- Right Join
Right join return rows which are common between the tables and all rows of Right hand side table. Simply, it returns all the rows from the right hand side table even though there are no matches in the left hand side table.
- Left Join
Left join return rows which are common between the tables and all rows of Left hand side table. Simply, it returns all the rows from Left hand side table even though there are no matches in the Right hand side table.
- Full Join
Full join return rows when there are matching rows in any one of the tables. This means, it returns all the rows from the left hand side table and all the rows from the right hand side table.
- What is a join?
This is a keyword used to query data from more tables based on the relationship between the fields of the tables. Keys play a major role when JOINs are used.
Normalization
Normalization is the process of minimizing redundancy and dependency by organizing fields and table of a database. The main aim of Normalization is to add, delete or modify field that can be made in a single table.
Denormalization
Denormalization is a technique used to access the data from higher to lower normal forms of database. It is also process of introducing redundancy into a table by incorporating data from the related tables.
Different Normalizations
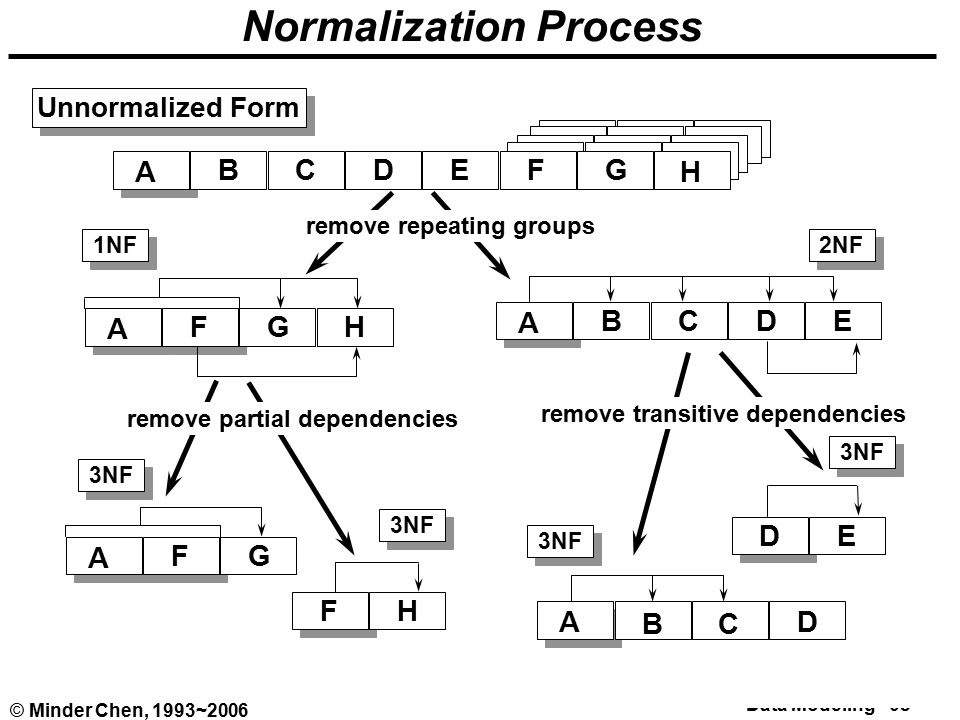

- First Normal Form (1NF):
This should remove all the duplicate columns from the table. Creation of tables for the related data and identification of unique columns.
- Second Normal Form (2NF):
Meeting all requirements of the first normal form. Placing the subsets of data in separate tables and Creation of relationships between the tables using primary keys.
- Third Normal Form (3NF):
This should meet all requirements of 2NF. Removing the columns which are not dependent on primary key constraints.
- Fourth Normal Form (3NF):
Meeting all the requirements of third normal form and it should not have multi- valued dependencies.
What I'll be doing tomorrow?
I will be continue doing the summary of the SQL because I got a really low mark on the quiz which is like 10%. So I decided to gather the notes of SQL and try memorize it then do the quiz again.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)