SQL Summary(1)
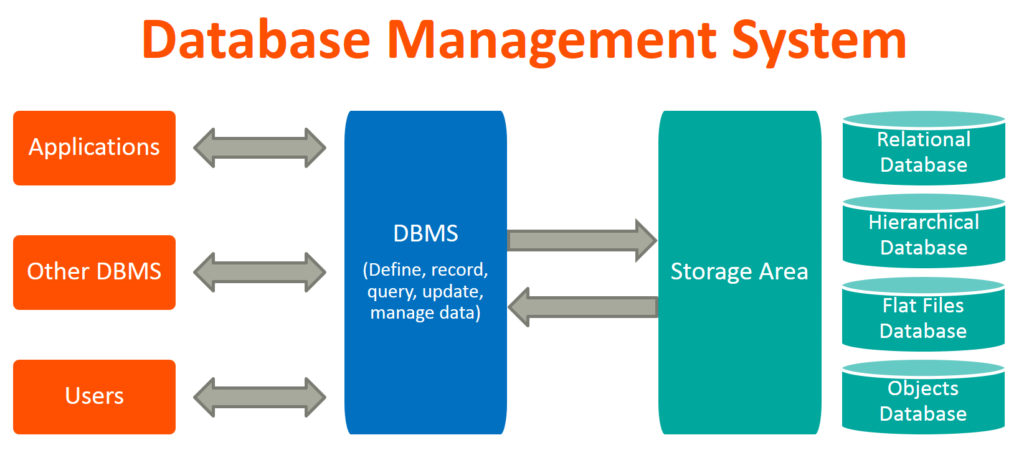
DBMS
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a program that controls creation, maintenance and use of a database. DBMS can be termed as File Manager that manages data in a database rather than saving it in file systems.
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. RDBMS store the data into the collection of tables, which is related by common fields between the columns of the table. It also provides relational operators to manipulate the data stored into the tables.
Database
Database is nothing but an organized form of data for easy access, storing, retrieval and managing of data. This is also known as structured form of data which can be accessed in many ways.
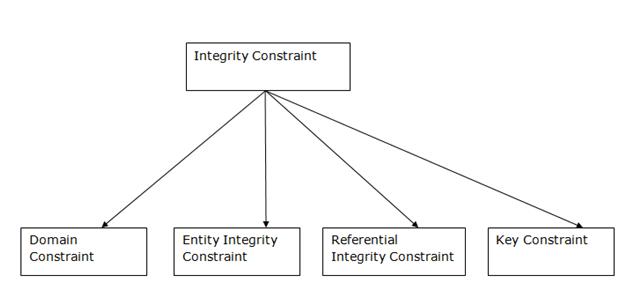
KEYS
A primary key is a combination of fields which uniquely specify a row. This is a special kind of unique key, and it has implicit NOT NULL constraint. It means, Primary key values cannot be NULL.
A Unique key constraint uniquely identified each record in the database. This provides uniqueness for the column or set of columns.
A foreign key is one table which can be related to the primary key of another table. Relationship needs to be created between two tables by referencing foreign key with the primary key of another table.
JOINS
Inner join return rows when there is at least one match of rows between the tables.
Right join return rows which are common between the tables and all rows of Right hand side table. Simply, it returns all the rows from the right hand side table even though there are no matches in the left hand side table.
Left join return rows which are common between the tables and all rows of Left hand side table. Simply, it returns all the rows from Left hand side table even though there are no matches in the Right hand side table.
Full join return rows when there are matching rows in any one of the tables. This means, it returns all the rows from the left hand side table and all the rows from the right hand side table.
This is a keyword used to query data from more tables based on the relationship between the fields of the tables. Keys play a major role when JOINs are used.
Normalization
Normalization is the process of minimizing redundancy and dependency by organizing fields and table of a database. The main aim of Normalization is to add, delete or modify field that can be made in a single table.
Denormalization
Denormalization is a technique used to access the data from higher to lower normal forms of database. It is also process of introducing redundancy into a table by incorporating data from the related tables.
Different Normalizations
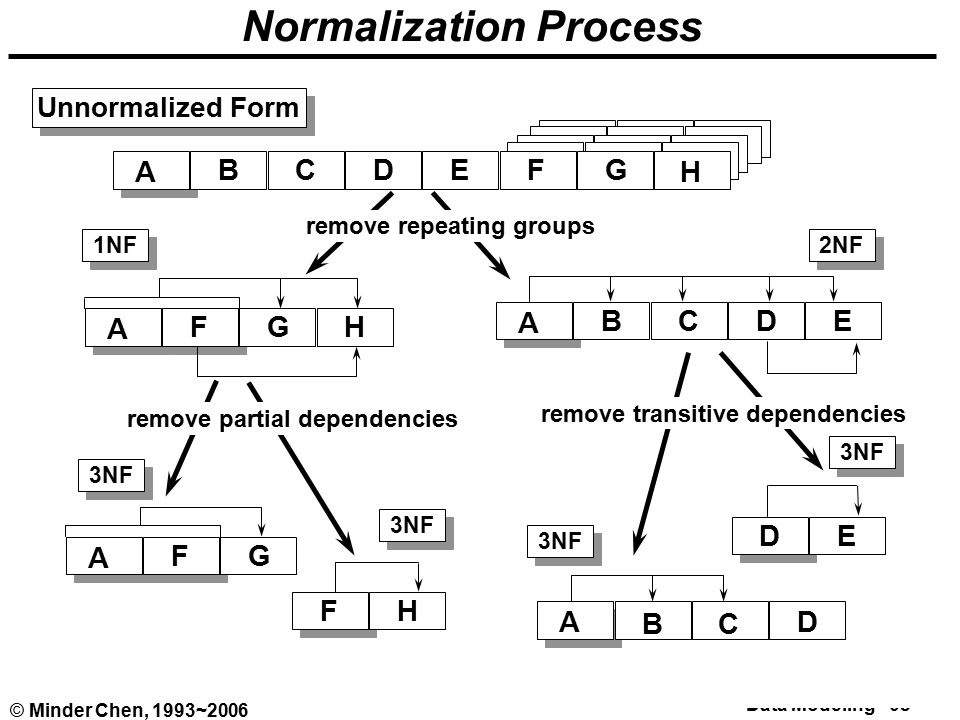
This should remove all the duplicate columns from the table. Creation of tables for the related data and identification of unique columns.
- Second Normal Form (2NF):
Meeting all requirements of the first normal form. Placing the subsets of data in separate tables and Creation of relationships between the tables using primary keys.
This should meet all requirements of 2NF. Removing the columns which are not dependent on primary key constraints.
- Fourth Normal Form (3NF):
Meeting all the requirements of third normal form and it should not have multi- valued dependencies.
What I'll be doing tomorrow?
I will be continue doing the summary of the SQL because I got a really low mark on the quiz which is like 10%. So I decided to gather the notes of SQL and try memorize it then do the quiz again.